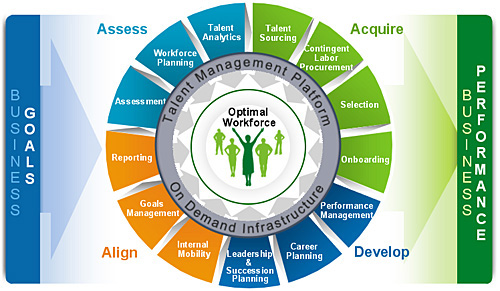
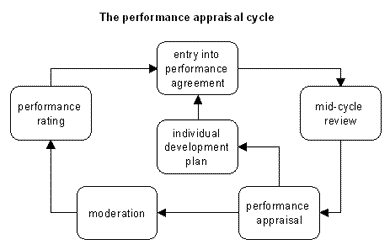
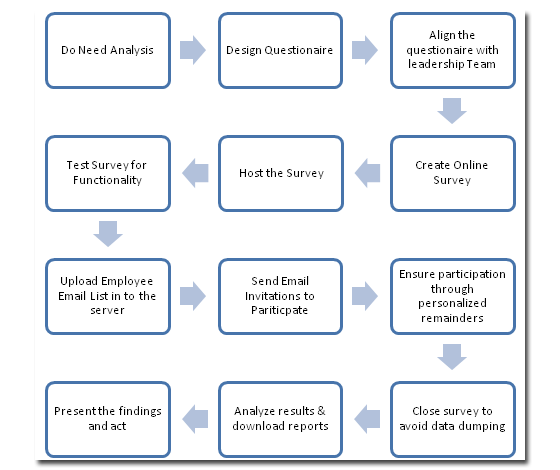
Human Resource is one of the mainly vital and incorporated divisions for any trade organization. It engages learning the special features of an organization in relation to its employees and also studies the workers on individual and cooperative basis. It typically engages indicators which are vital to recognize and examine; worker approaches, worker ability levels, worker earnings, recruitment procedure, training plans, promotions etc. These metrics relate to approximately seventy five percent of trades. Although the choice of building modified indicators is also accessible in the balanced scorecards.
Each of the indicators holds up to five act indicators like worker outlooks metric comprises; Job satisfaction, director satisfaction and so on as for worker earnings in typically fashions rate per hire, publicity, relocations, income rate, length of service etc. the key metrics for enlists comprise; vacant period, presentation assessment of the new employs monetary collision of poor employs.
Under the maintenance metrics worker income, avoidable earnings, the issue that studies causes why the worker left and managing procedures, variety income and monetary crash of worker earnings are measured. Diversity income takes into explanation portions as; specialized, administrative and industrial positions.
Being one of the most significant metrics, preparation and growth is given high significance to include indicators as; knowledge and expansion chances, number of workers pleased with the chances given, on-job guidance approval, new hires expansion chances etc.
in spite of the reality that although all associations use these ordinary position of HR metrics, the exceptionality that sets balanced scorecards separately is the mechanism of these metrics. For instance price per hire is a comprehensive look into the range of features of operating cost from; publicity to online services, surroundings checks to recruiter expenses.
In the similar way staffing and employment are given exact mechanism other than the ordinary ones to recognize the cause of employment and the growth of the personnel appoints through it.
Not just the associations, but the administration on the whole can gather the profits of balanced scorecards. It permits the higher administration the capability of on time evaluation to recognize areas of development in its human resource pond. It is a rapid method to recognize matters related to absence and output and save a trade unit from expensive operating cost. This
HR associated data is also functional in making monetary information in order to connect human possessions capacity to asset return. This data permits the change of human resource abilities to planned values which due to its currently enumerated nature becomes simple for convenience and readability. Balanced scorecards is a agenda planned to help association and the administration with the troubles that may be troubling their personnel and gives break by receiving to the origin of human supply management matters with additional viewpoint.